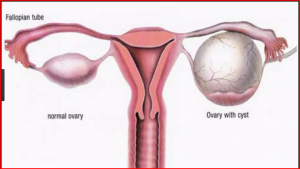
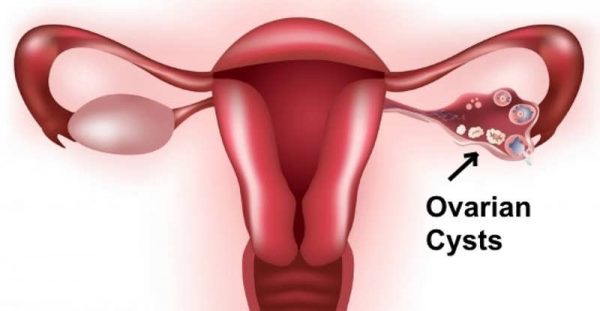
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Q1) I am 28 years old lady having 7 weeks of pregnancy. During the ultrasound, my doctor told me that I have a 4 cms ovarian cyst. I am really worried!
Most of the ovarian cysts diagnosed during pregnancy are (non-cancerous) benign and go away on their own. Your doctor will check it regularly and mostly you will not require any treatment. However, occasionally the cyst may have to be removed before your delivery.
Q2) My mother is 60 years old having menopause for 12 years. During her annual health check-up, she has been told that she has an ovarian cyst. Does she have cancer?
Ovarian cysts are common in post-menopausal women and most are not cancerous (benign). But considering her age the ovarian cyst should be evaluated by a gynecologist. Detailed sonography along with blood tests and clinical examination is to be done.
Q3) I am 28 years old and had one ovary removed one month back due to a big ovarian cyst. Can I still get pregnant?
Ovulation (the monthly release of the egg from an ovary) normally alternates between the two ovaries. When one is removed, the other ovary takes over the entire fertility function and your body should be producing the same amount of estrogen as it always did. Provided there are no other fertility issues, there should be no problem in conceiving.
Q4) I am a 40-year-old female having two kids. I was having pain abdomen for which my gynecologist advised an ultrasound. I have been diagnosed with a left ovarian cyst. My mother had ovarian cancer. Do I also have cancer?
You should consult your doctor to assess your risk. Clinical examination, a transvaginal ultrasound, and a CA125 blood test should be done. Genetic counseling and testing are done in women with a strong family history of ovarian cancer.
Q5) My daughter is 20 years old and unmarried. She has been diagnosed with an ovarian cyst of 12×10 cms. My doctor has advised her surgery. In which ovarian cysts is surgery required and can it be done laparoscopically?
Surgery is required if the ovarian cyst is very large, increasing in size, causes symptoms, undergoes torsion or there is suspicion of cancer. If the cyst seems benign, then it is removed laparoscopically (keyhole surgery). However, if there is suspicion of cancer then open surgery (by keeping an incision on the abdomen) can be done.